Fibonacci Numbers
The Fibonacci sequence is given by : 0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, …. By definition the Fibonacci sequence starts at 0 and 1 and each subsequent number is the sum of the previous two. In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci number is defined by the recurrence relation
\(F_n = Fn-1 + Fn-2\) with \(F0=0\) and \(F1=1\)
An algorithm for calculating the nth Fibonacci number can be implemented either recursively or iteratively.
These are examples for recursive and iterative fibonacci:
def rec_fib(n):
if (n == 0):
return 0
elif (n==1):
return 1
else:
return rec_fib(n-1)+rec_fib(n-2)
def iter_fib(n):
fib = 0
a = 1
t = 0
for k in range(1,n+1):
t = fib + a
a = fib
fib = t
return fibThe graph below shows the experiemental data from running the two algorithms.
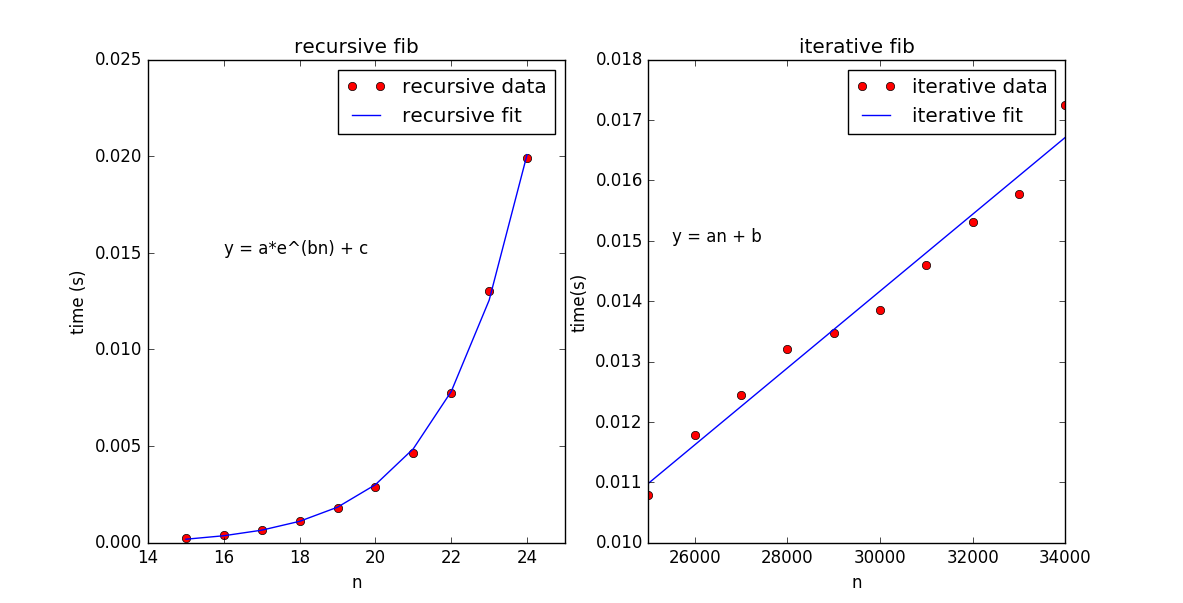
The main difference is how the recursive algorithm grows at exponential rate and shows the downside of the recursive algorithm. While the recursive algorithm is simple and elegant, it is also very time consuming.